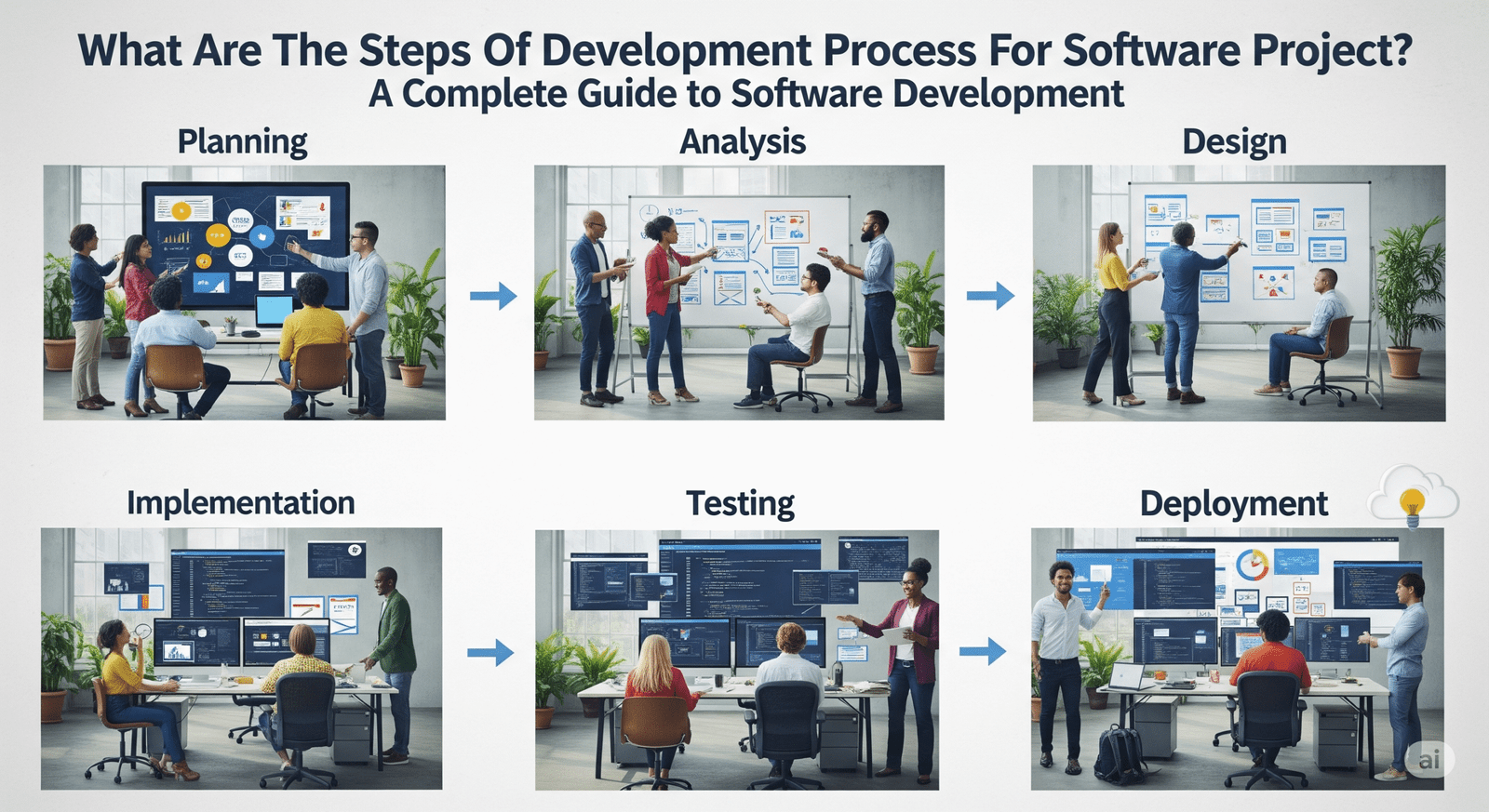
What Are The Steps Of Development Process For Software Project? A Complete Guide to Software Development
Software Development, Have you ever wondered how your favorite apps and software come to life? Whether it’s the social media platform you scroll through daily or that productivity app that keeps you organized, every piece of software follows a structured journey from idea to reality.
Understanding the software development process is crucial for anyone looking to build digital solutions, whether you’re an entrepreneur with the next big idea or a business owner seeking to digitize your operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through each step of the software development process, breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand insights that will help you navigate your next software project successfully.
Table of Contents
What is the Software Development Process?
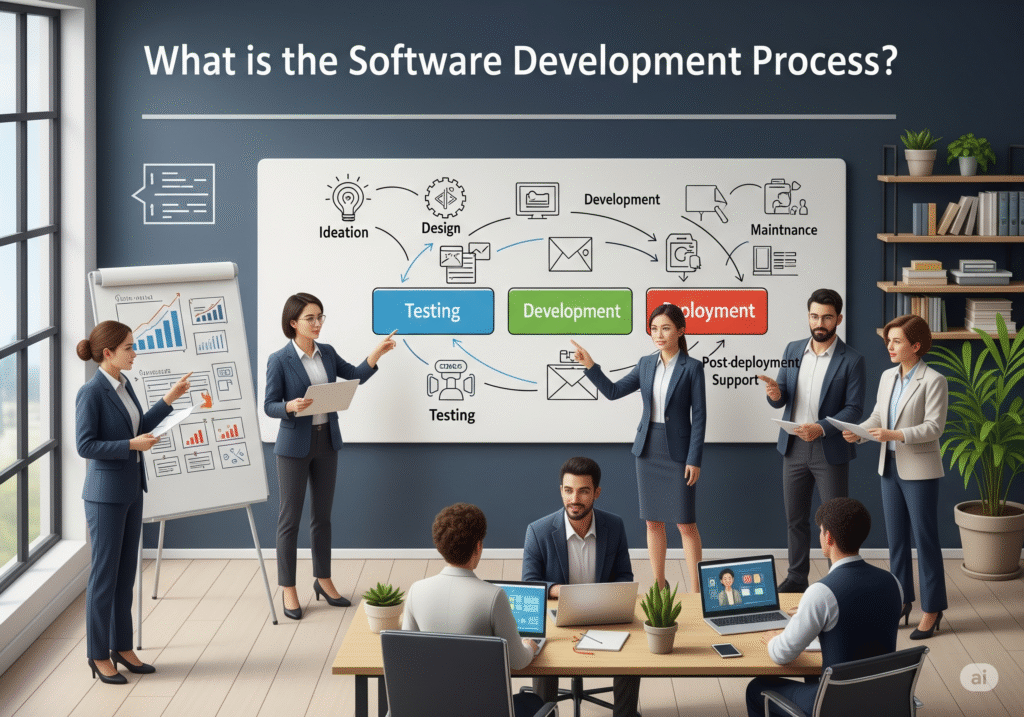
The software development process, also known as the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), is a systematic approach to creating software applications. Think of it as a roadmap that guides development teams from the initial concept to the final product launch and beyond.
This structured methodology ensures that software projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet user expectations. Without following these established steps, even the most brilliant software ideas can turn into costly failures.
According to industry research, projects that follow a structured development process have a 70% higher success rate compared to those that don’t.
Why Following a Structured Development Process Matters

Before diving into the specific steps, let’s understand why following a proper software development process is essential:
Risk Mitigation: A structured approach helps identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of project failure.
Cost Control: By planning thoroughly upfront, you avoid expensive changes and rework later in the project.
Quality Assurance: Each phase includes quality checkpoints, ensuring the final product meets high standards.
Better Communication: Clear phases and deliverables improve communication between team members and stakeholders.
Scalability: A well-planned architecture makes it easier to scale and maintain the software in the future.
Step 1: Planning and Requirement Analysis
The foundation of successful software development begins with thorough planning and requirement analysis. This crucial first step sets the direction for your entire project.
What Happens During Planning?
Requirement Gathering: Development teams work closely with stakeholders to understand exactly what the software needs to accomplish. This involves detailed discussions about features, functionality, and user expectations.
Market Research: Understanding your target audience and analyzing competitors helps shape the software’s direction and ensures market viability.
Feasibility Analysis: Teams evaluate whether the project is technically and financially viable given the available resources, timeline, and budget constraints.
Project Scope Definition: Clear boundaries are established regarding what will and won’t be included in the initial release, preventing scope creep later.
Resource Planning: Determining the team size, skill requirements, technology stack, and timeline needed for successful project completion.
Key Deliverables
- Detailed requirement specification document
- Project timeline and milestones
- Budget allocation and resource plan
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
Skipping or rushing through this phase is like building a house without blueprints – you might end up with something functional, but it probably won’t be what you envisioned.
Step 2: System Design
Once requirements are clear, the next step in the software development process involves creating a detailed blueprint of how the software will work. This phase transforms abstract requirements into concrete technical specifications.
High-Level Design (HLD)
The high-level design focuses on the overall system architecture:
System Architecture: Defining how different components will interact and communicate with each other.
Technology Stack Selection: Choosing the appropriate programming languages, frameworks, databases, and third-party services.
Integration Planning: Determining how the software will connect with existing systems, APIs, and external services.
Security Framework: Establishing security protocols and data protection measures from the ground up.
Low-Level Design (LLD)
The low-level design dives into specific implementation details:
Database Schema: Designing how data will be stored, organized, and accessed.
Module Specifications: Breaking down the system into smaller, manageable components with clear responsibilities.
User Interface Design: Creating wireframes and mockups that define the user experience.
API Documentation: Specifying how different parts of the system will communicate.
Why Good Design Matters
A well-thought-out design phase prevents major architectural changes during development, which can be extremely costly and time-consuming. Industry studies show that fixing a design flaw during development costs 10 times more than addressing it during the design phase.
Step 3: Implementation (Coding)
The implementation phase is where the magic happens – this is when your software development project starts taking tangible shape as developers begin writing code based on the designs and specifications created earlier.
Core Development Activities
Code Writing: Developers use the chosen programming languages and frameworks to build the software functionality according to specifications.
Version Control Implementation: Using tools like Git to track changes, manage different versions, and enable collaborative development without conflicts.
Code Review Process: Regular peer reviews ensure code quality, catch potential issues early, and maintain consistency across the team.
Documentation Creation: Writing clear documentation for code functions, APIs, and system components to facilitate future maintenance and updates.
Development Best Practices
Coding Standards: Following established conventions for naming, formatting, and structuring code makes it more readable and maintainable.
Modular Development: Breaking the software into smaller, independent modules that can be developed, tested, and maintained separately.
Regular Commits: Frequent code commits with clear descriptions help track progress and make it easier to identify and fix issues.
Collaborative Development: Using collaborative tools and practices that enable multiple developers to work efficiently without stepping on each other’s toes.
The implementation phase can be both exciting and challenging. Some days everything flows smoothly, while others might involve hunting down elusive bugs. However, with proper planning and good development practices, your software gradually transforms from concept to reality.
Step 4: Testing
No responsible software development process is complete without thorough testing. This critical phase ensures your software works correctly, securely, and provides a great user experience before it reaches your audience.
Types of Testing
Unit Testing: Individual components are tested in isolation to ensure they function correctly. Think of it as checking each ingredient before cooking a meal.
Integration Testing: After individual components work, they need to work together seamlessly. This phase tests how different modules interact and share data.
System Testing: The complete software is tested as a whole to verify it meets all specified requirements and functions properly in various scenarios.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Real users test the software and provide feedback, ensuring it meets their needs and expectations.
Performance Testing: Evaluating how the software performs under different loads and stress conditions to ensure it can handle real-world usage.
Security Testing: Identifying and addressing potential security vulnerabilities to protect user data and system integrity.
Benefits of Comprehensive Testing
Bug Prevention: Catching and fixing issues before launch prevents costly emergency fixes and protects your reputation.
User Satisfaction: Thorough testing ensures users have a smooth, frustration-free experience with your software.
Cost Savings: According to IBM research, fixing a bug during testing costs 15 times less than fixing it after deployment.
Performance Optimization: Testing helps identify bottlenecks and optimization opportunities before they impact users.
Step 5: Deployment
After successful testing, your software development project is ready for deployment – the exciting moment when your software goes live and becomes available to users.
Deployment Strategies
Big Bang Deployment: Releasing the entire system at once. This approach is simpler but carries higher risk if issues arise.
Phased Rollout: Gradually releasing features or rolling out to different user groups, allowing for controlled testing and feedback collection.
Beta Release: Launching to a limited group of users first to gather feedback and identify any remaining issues before full release.
Blue-Green Deployment: Maintaining two identical production environments to enable zero-downtime deployments and quick rollbacks if needed.
Deployment Checklist
Production Environment Setup: Configuring servers, databases, and all necessary infrastructure components for optimal performance and security.
Performance Monitoring: Implementing tools to track system performance, user behavior, and potential issues in real-time.
Backup and Recovery Plans: Establishing procedures to protect data and quickly recover from any unexpected problems.
User Training and Documentation: Providing users with the resources they need to effectively use the new software.
Support Team Preparation: Ensuring customer support teams are ready to help users and address any questions or issues.
Post-Deployment Monitoring
The work doesn’t stop once your software goes live. Continuous monitoring helps identify issues quickly and ensures optimal performance:
- Real-time performance tracking
- User behavior analysis
- Error monitoring and alerting
- Security monitoring
- Capacity planning and scaling
Step 6: Maintenance and Support
The final phase of the software development process focuses on keeping your software running smoothly and evolving with user needs. This ongoing phase is crucial for long-term success.
Types of Maintenance
Corrective Maintenance: Fixing bugs and issues that users discover after launch. No software is perfect, so having a process for quick issue resolution is essential.
Adaptive Maintenance: Updating the software to work with new operating systems, browsers, or third-party services as technology evolves.
Perfective Maintenance: Adding new features and improvements based on user feedback and changing business requirements.
Preventive Maintenance: Proactively updating code, security measures, and infrastructure to prevent future problems.
Ongoing Support Activities
Performance Monitoring: Continuously tracking system performance and optimizing as needed to handle growing user bases and changing usage patterns.
Security Updates: Regularly updating security measures and patching vulnerabilities to protect against evolving threats.
Feature Updates: Rolling out new functionality and improvements based on user feedback and market demands.
Technical Support: Providing users with help and guidance when they encounter issues or have questions.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Maintaining robust backup systems and recovery procedures to protect against data loss.
The Importance of Ongoing Maintenance
Companies that invest in proper maintenance see significant benefits:
- Higher user satisfaction and retention
- Better security and compliance
- Lower long-term costs
- Competitive advantage through continuous improvement
- Extended software lifespan and ROI
Research shows that maintenance typically accounts for 60-80% of the total software lifecycle cost, making it crucial to plan for this phase from the beginning.
Best Practices for Successful Software Development
Following these proven practices can significantly improve your software development project’s chances of success:
Communication and Collaboration
Regular Stand-ups: Daily or weekly team meetings keep everyone aligned and help identify blockers quickly.
Clear Documentation: Maintaining up-to-date documentation ensures knowledge sharing and easier onboarding of new team members.
Stakeholder Involvement: Regular check-ins with stakeholders prevent misaligned expectations and ensure the project stays on track.
Quality Assurance
Automated Testing: Implementing automated tests saves time and ensures consistent quality checks throughout development.
Code Reviews: Peer reviews catch issues early and promote knowledge sharing among team members.
Continuous Integration: Automatically integrating and testing code changes helps maintain code quality and catch integration issues quickly.
Project Management
Agile Methodology: Using iterative development approaches allows for flexibility and faster delivery of working software.
Risk Management: Regularly identifying and addressing potential risks prevents small issues from becoming major problems.
Progress Tracking: Using project management tools to track progress and identify potential delays early.
Technology Choices
Scalable Architecture: Designing systems that can grow with user demand prevents costly rewrites later.
Modern Technologies: Using current, well-supported technologies ensures better performance and easier maintenance.
Security First: Building security considerations into every phase rather than treating it as an afterthought.
How to Choose the Right Development Partner
Selecting the right partner for your software development project can make the difference between success and failure. Here’s what to look for:
Technical Expertise
Relevant Experience: Look for teams with proven experience in your industry and with similar project types.
Technology Proficiency: Ensure they’re skilled in the technologies that best fit your project requirements.
Quality Standards: Ask about their development processes, testing procedures, and quality assurance practices.
Communication and Collaboration
Clear Communication: Choose partners who communicate clearly and regularly throughout the project.
Project Management: Look for teams that use modern project management tools and methodologies.
Cultural Fit: Ensure their working style and values align with your organization’s culture.
Support and Maintenance
Long-term Partnership: Select partners who offer ongoing support and maintenance services.
Scalability: Ensure they can scale their team up or down based on your project needs.
Response Time: Verify their commitment to timely responses and issue resolution.

YAAM Web Solutions: Your Software Development Partner
Creating successful software requires expertise across all phases of the development lifecycle. That’s where YAAM Web Solutions comes in.
Our team specializes in delivering high-quality software development solutions that bring your vision to life. Whether you’re a startup with an innovative idea, an enterprise looking to modernize systems, or a growing business seeking digital transformation, we ensure your project succeeds.
What We Offer
Custom Software Development: Tailored solutions built specifically for your unique business requirements and goals.
End-to-End SDLC Management: Complete project management from initial planning through deployment and ongoing maintenance.
Modern Technology Stack: Expertise in the latest technologies and frameworks to build scalable, secure, and high-performance software.
Agile Development Process: Flexible, iterative approach that delivers working software quickly and adapts to changing requirements.
Quality Assurance: Comprehensive testing and quality control processes to ensure reliable, bug-free software.
Ongoing Support: Long-term partnership with maintenance, updates, and technical support to keep your software running smoothly.
Why Choose YAAM Web Solutions?
Proven Track Record: Years of experience delivering successful software projects across various industries.
Expert Team: Skilled developers, designers, and project managers with deep technical expertise.
Client-Focused Approach: We prioritize understanding your business needs and delivering solutions that drive real value.
Transparent Process: Regular communication, clear timelines, and detailed progress reporting throughout your project.
Competitive Pricing: High-quality development services at competitive rates with flexible engagement models.
Ready to turn your software idea into reality? Contact YAAM Web Solutions today to discuss your project and discover how we can help you succeed.
Conclusion
Understanding the steps of the software development process is essential for anyone embarking on a software project. From initial planning and requirement analysis through design, implementation, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance, each phase plays a crucial role in creating successful software.
The key to success lies in following a structured approach, maintaining clear communication, focusing on quality, and partnering with experienced professionals who understand the complexities of modern software development.
Remember that software development is not just about writing code – it’s about solving real problems for real people. By following the structured process outlined in this guide and working with the right development partner, you can transform your software ideas into powerful solutions that make a meaningful impact.
Whether you’re planning your first software project or looking to improve your development process, the principles and practices covered in this guide will help you navigate the journey from concept to successful software launch and beyond.
Ready to start your software development journey? The team at YAAM Web Solutions is here to help you every step of the way. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can bring your vision to life.